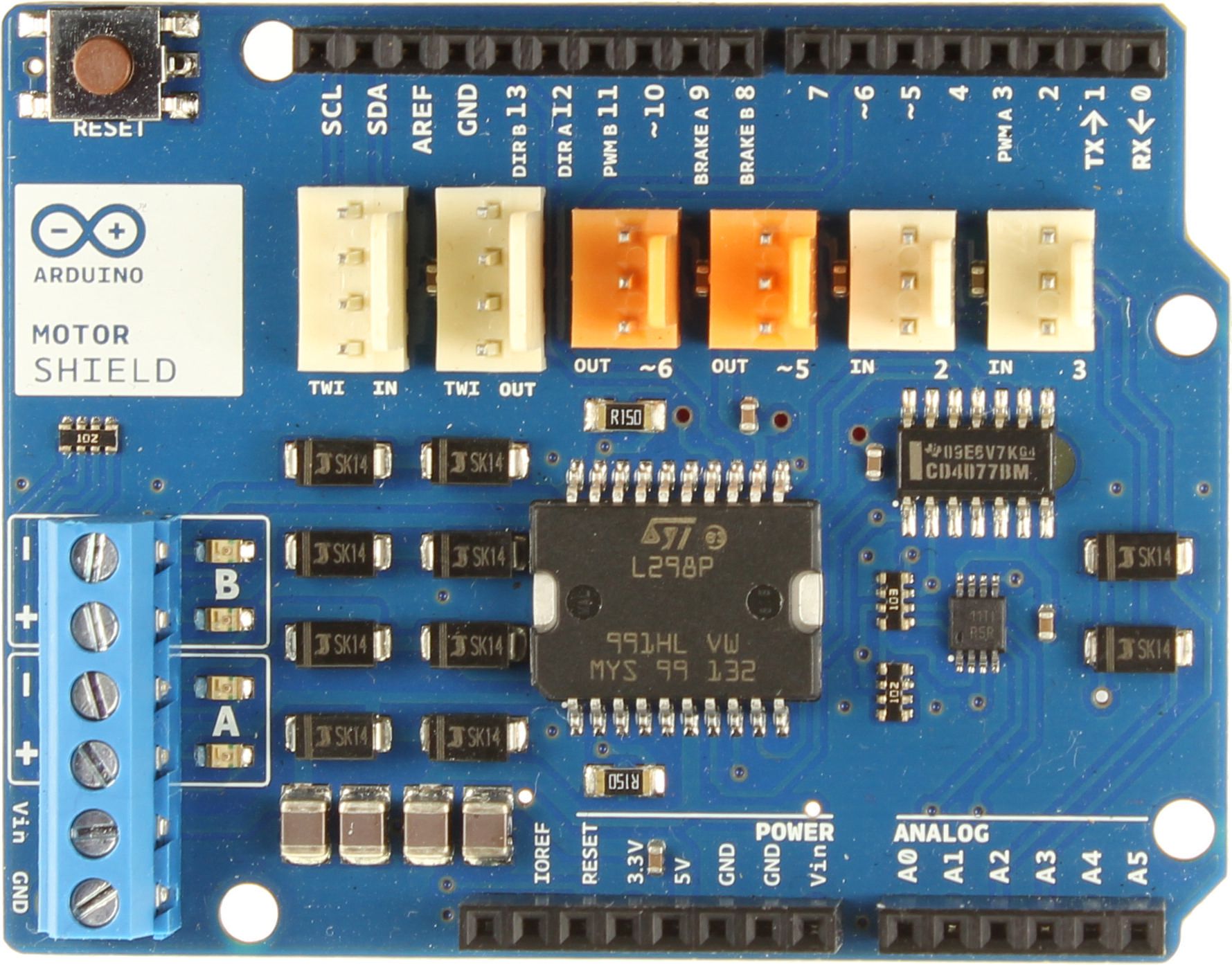
El oficial Arduino Motor Shield es una placa de expansión para los microcontroladores Arduino UNO y Mega para el control de motores de corriente continua y paso a paso. Hemos visto cómo conducir un motor de corriente continua usando un puente H que puede requerir mucho cableado cuando se usa el IC simplemente. Para una aplicación incorporada, como un robot Willy, tendrás que accionar varios motores en paralelo. Hay escudos disponibles para simplificar el montaje.
Hardware
- Computadora
- Arduino UNO
- Cable USB A macho a B macho
- Arduino Motor Shield
- Motor DC x1 o Motor paso a paso x1
Principio de funcionamiento
El Motor Shield Arduino utiliza el doble puente H del L298. Permite accionar los motores en dirección y velocidad con una tensión nominal entre 5 y 12V y una corriente de 2A, hasta 4A con una fuente de tensión externa.
Este escudo permite controlar:
- hasta dos motores de corriente continua o un motor de paso bipolar
- dos sensores analógicos
- dos salidas PWM como servomotores.
- hay disponible un bus I2C que permite la conexión de módulos compatibles
Esquema
Compatible con las tarjetas UNO y Mega, el escudo se coloca directamente en la tarjeta Arduino. La fuente de alimentación está conectada al bloque de terminales de energía. Los motores están conectados a los terminales A+, A-, B+, B-. Los pines del Arduino están directamente conectados a los pines del circuito integrado:
- Digital pin 12: direction DC Motor #A / Stepper #A
- Digital pin 13: direction DC Motor #B / Stepper #B
- Digital pin 3: vitesse DC Motor #A / Stepper #A
- Digital pin 11: vitesse DC Motor #B / Stepper #B
- Digital pin 9: activation brake DC Motor #A
- Digital pin 8: activation brake DC Motor #B
- Entradas disponibles In2 In3 conectadas a las entradas analógicas A2 y A3
- Salidas disponibles Out5, Out6 conectadas a las salidas PWM 5 y 6
En el caso de un escudo, las conexiones están predefinidas. Revise la documentación técnica del componente para ver cómo se utiliza.
Las conexiones del motor se detallan en los siguientes diagramas.
Código
Para interactuar con el Motor Shield, no usamos una biblioteca especial porque está conectada a los pines de Arduino directamente. Siempre puedes crear tu propia biblioteca para simplificar tu código.
//Parameters
const int input_voltage = 9;//V
const int nominal_voltage = 5;////V
const int MAX_SPEED = int(nominal_voltage * 255 / input_voltage);
const int directionA = 12;
const int directionB = 13;
const int brakeA = 9;
const int brakeB = 8;
const int speedA = 3;
const int speedB = 11;
const int in2 = A2;
const int in3 = A3;
void setup() {
//Init Serial USB
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("Initialize System"));
//Init Motor Shield
pinMode(directionA, OUTPUT); //Initiates Motor Channel A pin
pinMode(brakeA, OUTPUT); //Initiates Brake Channel A pin
pinMode(directionB, OUTPUT); //Initiates Motor Channel B pin
pinMode(brakeB, OUTPUT); //Initiates Brake Channel B pin
}
void loop() {
readSensorMS();
testMotorMS();
//testStepperMS();
}
void testStepperMS() { /* function testStepperMS */
//// Test stepper
Serial.println("Move stepper 1 step clockwise");
stpCW(1);
Serial.println("Move stepper 1 step counter clockwise");
stpCCW(1);
}
void testMotorMS() { /* function testMotorMS */
//// Test DC motor
Serial.println(F("-------------------------------------"));
Serial.println(F("Avant "));
dcForward();
delay(500);
Serial.println(F("Arrière "));
dcBackward();
delay(500);
Serial.println(F("Arrêt "));
dcStop();
delay(1000);
}
void readSensorMS() { /* function readSensorMS */
//// Read sensors
Serial.print(F("In2 : ")); Serial.println(analogRead(in2));
Serial.print(F("In3 : ")); Serial.println(analogRead(in3));
}
void dcForward() { /* function dcForward */
//// set forward motion for A and B
digitalWrite(directionA, HIGH); //Establishes forward direction of Channel A
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disengage the Brake for Channel A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED);
digitalWrite(directionB, HIGH); //Establishes forward direction of Channel B
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disengage the Brake for Channel B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED);
}
void dcBackward() { /* function dcBackward */
//// set backward motion for A and B
digitalWrite(directionA, LOW); //Establishes forward direction of Channel A
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disengage the Brake for Channel A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED);
digitalWrite(directionB, LOW); //Establishes forward direction of Channel B
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disengage the Brake for Channel B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED);
}
void dcStop() { /* function dcStop */
//// stop motors A and B
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Engage the Brake for Channel A
analogWrite(speedA, 0);
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Engage the Brake for Channel B
analogWrite(speedB, 0);
}
void stpCW(int nbstep) { /* function stpCW */
//// Move stepper clockwise
for (int i = 0; i < nbstep; i++) {
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Enable brake B
digitalWrite(directionA, HIGH); //Set direction of CH A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH A
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Enable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disable brake B
digitalWrite(directionB, LOW); //Set direction of CH B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH B
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Enable brake B
digitalWrite(directionA, LOW); //Set direction of CH A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH A
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Enable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disable brake B
digitalWrite(directionB, HIGH); //Set direction of CH B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH B
delay(30);
}
}
void stpCCW(int nbstep) { /* function stpCCW */
//// Move stepper counter-clockwise
for (int i = 0; i < nbstep; i++) {
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Enable brake B
digitalWrite(directionA, HIGH); //Set direction of CH A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH A
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Enable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disable brake B
digitalWrite(directionB, HIGH); //Set direction of CH B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH B
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, LOW); //Disable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Enable brake B
digitalWrite(directionA, LOW); //Set direction of CH A
analogWrite(speedA, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH A
delay(30);
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Enable brake A
digitalWrite(brakeB, LOW); //Disable brake B
digitalWrite(directionB, LOW); //Set direction of CH B
analogWrite(speedB, MAX_SPEED); //Set speed for CH B
delay(30);
}
}
void dcStop() { /* function dcStop */
//// stop motors A and B
digitalWrite(brakeA, HIGH); //Engage the Brake for Channel A
analogWrite(speedA, 0);
digitalWrite(brakeB, HIGH); //Engage the Brake for Channel B
analogWrite(speedB, 0);
}
Aplicaciones
- Pilotar un robot de dos ruedas como Willy
Fuentes
Encuentre otros tutoriales y ejemplos en el generador de código automático
Arquitecto de Código