Neste tutorial, vamos aprender a ativar, gerir e testar o Bluetooth num ESP32 utilizando a linguagem de programação Arduino. O Bluetooth é uma tecnologia sem fios muito utilizada para a comunicação entre dispositivos electrónicos. Pode transformar rapidamente o seu sistema num objeto ligado.
Equipamento
- Um módulo ESP32 (Bluetooth+Wifi integrados)
- Um computador com Python instalado ou um smartphone
- Cabo USB para ligação ao computador ESP32
Configuração do ambiente e do IDE
Para programar o seu ESP32 com o IDE Arduino, pode seguir este tutorial anterior.
Recuperar o endereço MAC
Esta informação não é necessariamente necessária, mas é sempre uma boa ideia saber como obter o endereço MAC do ESP32.
#include "esp_bt_main.h"
#include "esp_bt_device.h"
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
void printDeviceAddress() {
const uint8_t* point = esp_bt_dev_get_address();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
char str[3];
sprintf(str, "%02X", (int)point[i]);
Serial.print(str);
if (i < 5){
Serial.print(":");
}
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SerialBT.begin("ESP32BT");
Serial.print("MaxAddr : ");
printDeviceAddress();
}
void loop() {}
Saída
14:42:43.448 -> MaxAddr : 3C:61:05:31:5F:12
Comunicação em série via Bluetooth
A comunicação Bluetooth é activada da mesma forma que a comunicação em série. O método é semelhante para o módulo HC-06
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
#error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
#endif
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SerialBT.begin("ESP32BT"); //Bluetooth device name
Serial.println("The device started, now you can pair it with bluetooth!");
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
SerialBT.write(Serial.read());
}
if (SerialBT.available()) {
Serial.write(SerialBT.read());
}
delay(20);
}
N.B.: Parece haver uma forma de adicionar um código PIN, mas não consigo pô-lo a funcionar.
SerialBT.setPin(pin);SerialBT.begin("ESP32BT ", true);
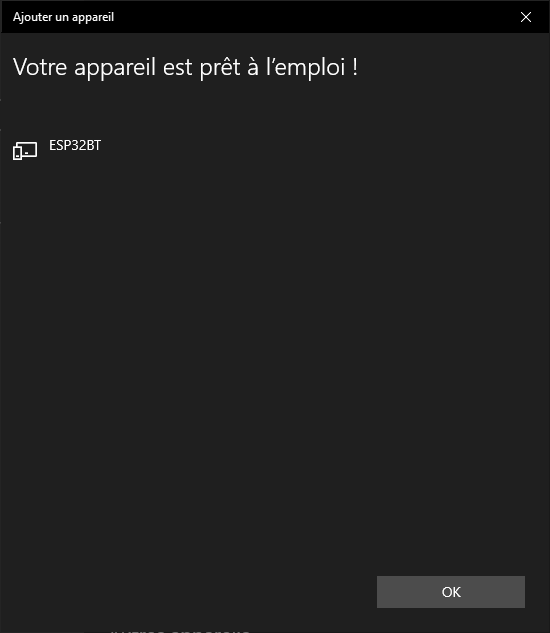
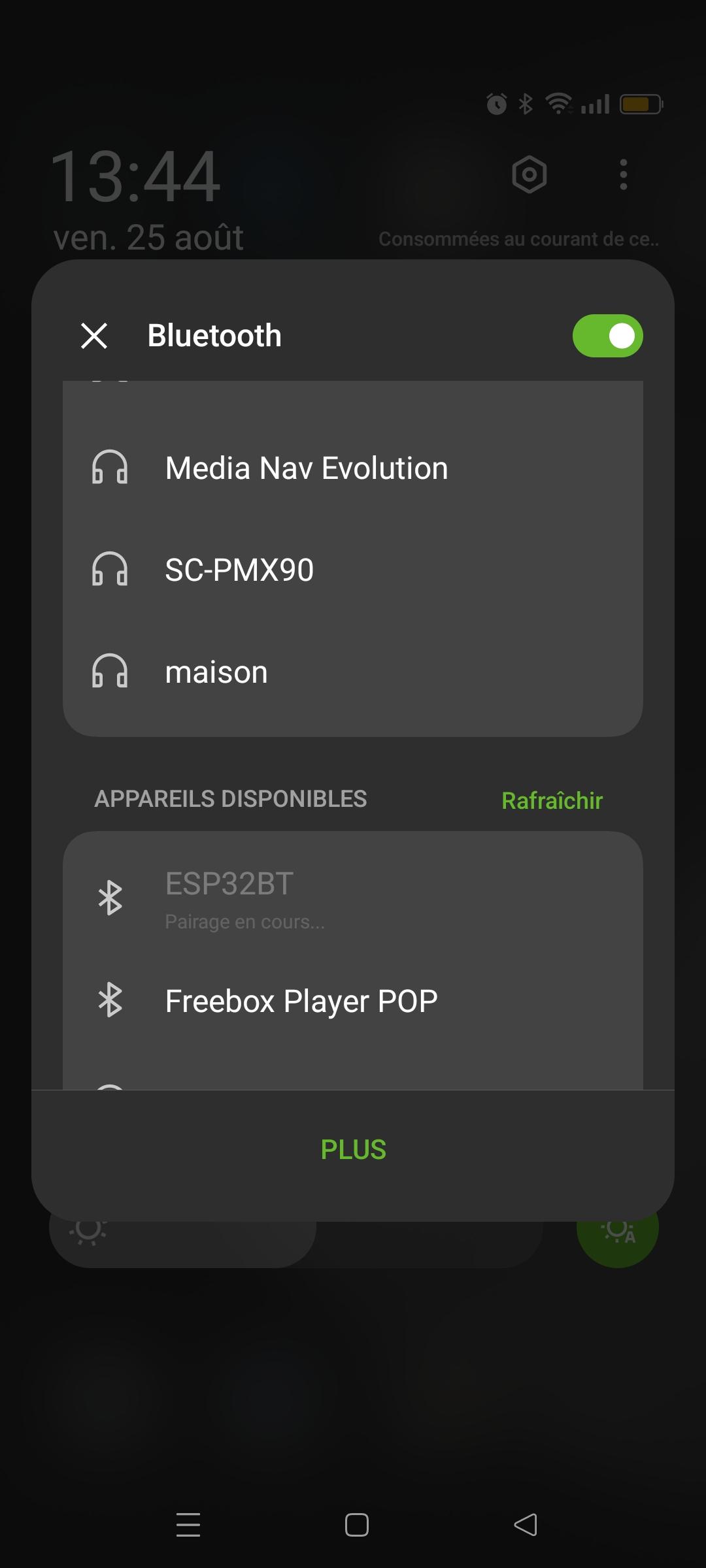
Emparelhamento
Uma vez configurado o módulo, pode emparelhar o ESP32 com o sistema da sua escolha, como qualquer outro dispositivo Bluetooth. Seleccione o nome na lista de dispositivos detectados (nome ESP32BT)
Teste da comunicação Bluetooth utilizando o terminal Bluetooth de série
Vamos testar a comunicação Bluetooth utilizando a aplicação Serial Terminal Bluetooth.

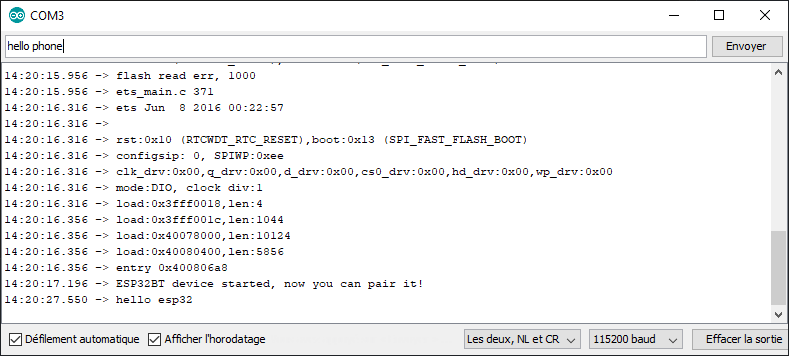
A mensagem é trocada entre o telemóvel e o ESP32 através de Bluetooth
Código para obter a encomenda completa
No código anterior, copiámos a mensagem byte a byte para a enviar de volta para o monitor. Aqui vamos registar o comando completo numa String msg. Isto permitir-lhe-á analisar o comando e definir a ação correspondente (por exemplo, ligar
#include "BluetoothSerial.h"
#if !defined(CONFIG_BT_ENABLED) || !defined(CONFIG_BLUEDROID_ENABLED)
#error Bluetooth is not enabled! Please run `make menuconfig` to and enable it
#endif
String msg;
BluetoothSerial SerialBT;
const char *pin = "1234";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
SerialBT.begin("ESP32BT"); //Bluetooth device name
Serial.println("ESP32BT device started, now you can pair it!");
}
void loop(){
readSerialPort();
// Send answer to master
if(msg!=""){
Serial.print("Master sent : " );
Serial.println(msg);
SerialBT.print("received : "+msg);
msg="";
}
}
void readSerialPort(){
while (SerialBT.available()) {
delay(10);
if (SerialBT.available() >0) {
char c = SerialBT.read(); //gets one byte from serial buffer
msg += c; //makes the string readString
}
}
SerialBT.flush();
}

Comunicação entre o ESP32 e o Python via Bluetooth
Pode gerir a comunicação Bluetooth a partir do seu PC.
Para fazer isso, instale o pacote PyBluez
python -m pip install pybluez
Detetar dispositivos bluetooth
import bluetooth
target_name = "ESP32BT"
target_address = None
nearby_devices = bluetooth.discover_devices(lookup_names=True,lookup_class=True)
print(nearby_devices)
for btaddr, btname, btclass in nearby_devices:
if target_name == btname:
target_address = btaddr
break
if target_address is not None:
print("found target {} bluetooth device with address {} ".format(target_name,target_address))
else:
print("could not find target bluetooth device nearby")
Saída
[('88:C6:26:91:30:84', 'UE\xa0BOOM\xa02', 2360344), ('88:C6:26:7E:F2:7A', 'UE\xa0BOOM\xa02', 2360344), ('4C:EA:AE:D6:92:08', 'OPPO A94 5G', 5898764), ('41:42:DD:1F:45:69', 'MX_light', 2360344), ('3C:61:05:31:5F:12', 'ESP32BT', 7936)]
found target ESP32BT bluetooth device with address 3C:61:05:31:5F:12
Ligação e comunicação com o ESP32
Aqui está um script Python para se ligar automaticamente ao dispositivo Bluetooth ESP32 a partir de um PC
import bluetooth
import socket
target_name = "ESP32BT"
target_address = None
nearby_devices = bluetooth.discover_devices(lookup_names=True,lookup_class=True)
print(nearby_devices)
for btaddr, btname, btclass in nearby_devices:
if target_name == btname:
target_address = btaddr
break
if target_address is not None:
print("found target {} bluetooth device with address {} ".format(target_name,target_address))
""" # With PyBluez NOT WORKING
serverMACAddress = target_address
port = 1
s = bluetooth.BluetoothSocket(bluetooth.RFCOMM)
s.connect((serverMACAddress, port))
while 1:
text = raw_input() # Note change to the old (Python 2) raw_input
if text == "quit":
break
s.send(text)
data = s.recv(1024)
if data:
print(data)
sock.close()"""
serverMACAddress = target_address
port = 1
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_BLUETOOTH, socket.SOCK_STREAM, socket.BTPROTO_RFCOMM)
s.connect((serverMACAddress,port))
print("connected to {}".format(target_name))
while 1:
text = input()
if text == "quit":
break
s.send(bytes(text, 'UTF-8'))
data = s.recv(1024)
if data:
print(data)
s.close()
else:
print("could not find target bluetooth device nearby")
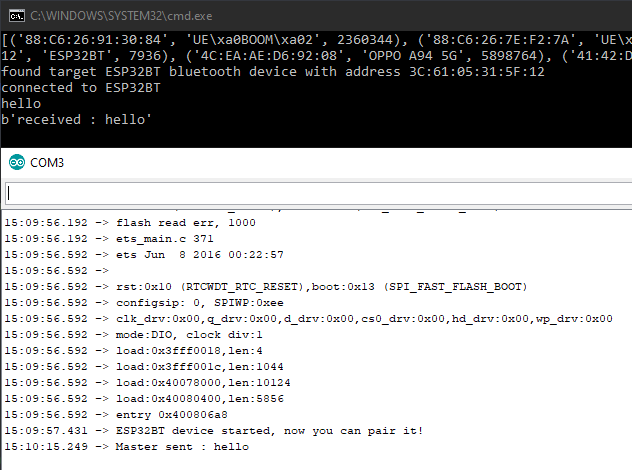
N.B.: Apenas a biblioteca socket funciona para a comunicação Bluetooth. Parece haver um problema de manutenção com a biblioteca PyBluez.