Neste tutorial, veremos como configurar um menu de navegação com diferentes telas no React Native. Para fazer isso, vamos usar a biblioteca React Navigation
N.B.: Existe outra alternativa react-native-navigation, mas não funciona no meu ambiente.
Configurar o projeto React Native
npm install @react-navigation/native npm install @react-navigation/native-stack
Em seguida, instale os seguintes pacotes
npm install --save react-native-screens react-native-safe-area-context
Para utilizar a navegação, é necessário atualizar o ficheiro MainActivity.java
android/app/src/main/java/<your package name>/MainActivity.javaAdicionar import android.os.Bundle; no início do ficheiro
e a função onCreate na classe MainActivity
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(null);
}
MainActivity.java
package com.menuapp;
import com.facebook.react.ReactActivity;
import com.facebook.react.ReactActivityDelegate;
import com.facebook.react.defaults.DefaultNewArchitectureEntryPoint;
import com.facebook.react.defaults.DefaultReactActivityDelegate;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends ReactActivity {
/**
* Returns the name of the main component registered from JavaScript. This is used to schedule
* rendering of the component.
*/
@Override
protected String getMainComponentName() {
return "MenuApp";
}
/**
* Returns the instance of the {@link ReactActivityDelegate}. Here we use a util class {@link
* DefaultReactActivityDelegate} which allows you to easily enable Fabric and Concurrent React
* (aka React 18) with two boolean flags.
*/
@Override
protected ReactActivityDelegate createReactActivityDelegate() {
return new DefaultReactActivityDelegate(
this,
getMainComponentName(),
// If you opted-in for the New Architecture, we enable the Fabric Renderer.
DefaultNewArchitectureEntryPoint.getFabricEnabled());
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(null);
}
}
Código da aplicação principal
No código principal da aplicação, index.js ou App.tsx, importamos o objeto NavigationContainer. Para o utilizar, basta rodear o código de renderização com a etiqueta correspondente. Neste exemplo, definimos duas páginas, cada uma com um botão que lhe permite ir para a outra página.
import * as React from 'react';
import { View, Button, Text } from 'react-native';
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { createNativeStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/native-stack';
function HomeScreen({ navigation }) {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center' }}>
<Text>Home Screen</Text>
<Button
title="Go to Details"
onPress={() => navigation.navigate('Details')}
/>
</View>
);
}
function DetailsScreen({ navigation }) {
return (
<View style={{ flex: 1, alignItems: 'center', justifyContent: 'center' }}>
<Text>Details Screen</Text>
<Button
title="Go to Details... again"
onPress={() => navigation.push('Details')}
/>
<Button title="Go to Home" onPress={() => navigation.navigate('Home')} />
<Button title="Go back" onPress={() => navigation.goBack()} />
</View>
);
}
const Stack = createNativeStackNavigator();
function App() {
return (
<NavigationContainer>
<Stack.Navigator initialRouteName="Home">
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} options={{ headerShown: false }}/>
<Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} />
</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
export default App;
Nota: pode escolher se quer ou não mostrar a barra de navegação utilizando a opção headerShown: false.
Exemplo: Criar um menu
Neste exemplo, vamos criar uma aplicação simples para apresentar diferentes ecrãs. Estes ecrãs baseiam-se no mesmo componente, que é adaptado de acordo com a informação contida numa lista.
Primeiro, criamos uma matriz que contém todas as informações de que precisamos
const screensArr = [
{
id: 1,
color: "blue",
text: "Screen 1",
items: ["item1","item2"]
},
{
id: 2,
color: "red",
text: "Screen 2",
items: ["item2","item3"]
},
{
id: 3,
color: "green",
text: "Screen 3",
items: ["item1","item2","item3"]
},
];
Componente principal
No componente principal, criamos uma lista de ecrãs Stack.Screen a partir do Array screensArr
const Stack = createNativeStackNavigator();
function App() {
const screensListArr = screensArr.map(buttonInfo => (
<Stack.Screen
key={buttonInfo.id}
name={buttonInfo.text}
component={DetailsScreen}
options={{
headerStyle: {
backgroundColor: buttonInfo.color,
},
headerTintColor: '#fff',
headerTitleStyle: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
}}
/>
));
return (
<NavigationContainer>
<Stack.Navigator initialRouteName="Home">
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} options={{ headerShown: false }}/>
{/*<Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} />*/}
{screensListArr}
</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
export default App;
Ecrã inicial
Em seguida, criamos o ecrã principal, que contém os botões para navegar para os outros ecrãs
Neste ecrã, adicionamos um botão para cada ecrã utilizando a função buttonListArr, que personalizamos com os dados contidos em screensArr.
function HomeScreen({ navigation }) {
const menuItemClick = (buttonInfo: { id: any; color?: string; text: any; }) => {
console.log(buttonInfo.id,' clicked :',buttonInfo.text);
navigation.navigate(buttonInfo.text,buttonInfo); //'Details')
};
const buttonsListArr = screensArr.map(buttonInfo => (
<Button
key={buttonInfo.id}
text={buttonInfo.text}
onPress={() => menuItemClick(buttonInfo)}
btnStyle={[styles.menuBtn,{backgroundColor:buttonInfo.color}]}
btnTextStyle={styles.menuText}
/>
));
return (
<ScrollView>
<View style={styles.mainBody}>
{buttonsListArr}
</View>
</ScrollView>
);
}
N.B.: note-se que existe uma única função para gerir vários botões menuItemClick(buttonInfo).
Ecrã de pormenor
Por fim, criamos a função DetailsScreen, que conterá as informações a apresentar para cada página.
Passamos os parâmetros da página quando chamamos a mudança de página
navigation.navigate(buttonInfo.text,buttonInfo); const buttonInfo = route.params;
function DetailsScreen({ route, navigation }) {
const buttonInfo = route.params;
const itemsListArr = buttonInfo.items.map(item => (
<View key={item} style={{marginTop:10,marginBottom:10,flexDirection:'row', width: "100%", borderBottomWidth: 1,borderBottomColor:"white",}} >
<Text style={{marginBottom:5,fontSize: 20,}}>{item}</Text>
</View>
));
return (
<View style={{
flex: 1,
//justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
//minHeight: windowHeight,
color: "white",
backgroundColor: "black",
}}>
{itemsListArr}
{/*<Button text="Go back" btnStyle={styles.deviceButton} btnTextStyle={styles.buttonText} onPress={() => navigation.goBack()} />*/}
</View>
);
}
Resultados
Depois de a aplicação ter sido compilada e carregada no dispositivo, podemos navegar de um ecrã para outro.
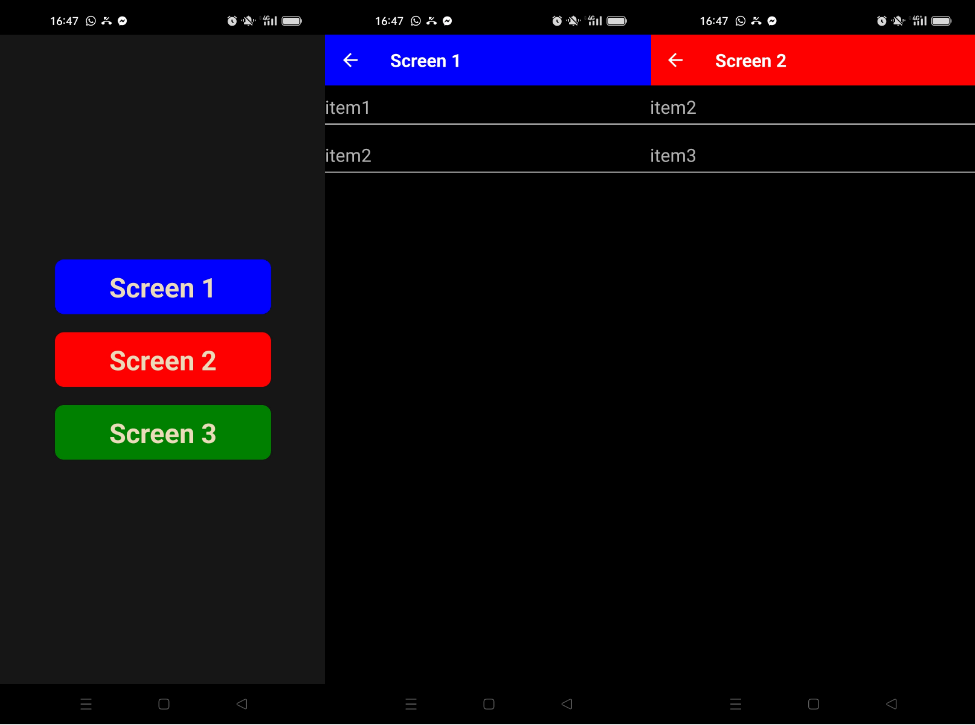
Código de exemplo completo
App.tsx
/**
* npm install --save react-native-navigation NOK
* npm install @react-navigation/native
* npm install @react-navigation/native-stack
* https://reactnavigation.org/docs/getting-started
*/
import React from 'react';
import {
View,
Text,
ScrollView,
} from 'react-native';
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native';
import { createNativeStackNavigator } from '@react-navigation/native-stack';
import Button from './src/ui_comp';
import {styles} from './src/styles/styles';
const screensArr = [
{
id: 1,
color: "blue",
text: "Screen 1",
items: ["item1","item2"]
},
{
id: 2,
color: "red",
text: "Screen 2",
items: ["item2","item3"]
},
{
id: 3,
color: "green",
text: "Screen 3",
items: ["item1","item2","item3"]
},
];
function HomeScreen({ navigation }) {
const menuItemClick = (buttonInfo: { id: any; color?: string; text: any; }) => {
console.log(buttonInfo.id,' clicked :',buttonInfo.text);
navigation.navigate(buttonInfo.text,buttonInfo); //'Details')
};
const buttonsListArr = screensArr.map(buttonInfo => (
<Button
key={buttonInfo.id}
text={buttonInfo.text}
onPress={() => menuItemClick(buttonInfo)}
btnStyle={[styles.menuBtn,{backgroundColor:buttonInfo.color}]}
btnTextStyle={styles.menuText}
/>
));
return (
<ScrollView>
<View style={styles.mainBody}>
{buttonsListArr}
</View>
</ScrollView>
);
}
function DetailsScreen({ route, navigation }) {
const buttonInfo = route.params;
const itemsListArr = buttonInfo.items.map(item => (
<View key={item} style={{marginTop:10,marginBottom:10,flexDirection:'row', width: "100%", borderBottomWidth: 1,borderBottomColor:"white",}} >
<Text style={{marginBottom:5,fontSize: 20,}}>{item}</Text>
</View>
));
return (
<View style={{
flex: 1,
//justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
//minHeight: windowHeight,
color: "white",
backgroundColor: "black",
}}>
{itemsListArr}
{/*<Button text="Go back" btnStyle={styles.deviceButton} btnTextStyle={styles.buttonText} onPress={() => navigation.goBack()} />*/}
</View>
);
}
const Stack = createNativeStackNavigator();
function App() {
const screensListArr = screensArr.map(buttonInfo => (
<Stack.Screen
key={buttonInfo.id}
name={buttonInfo.text}
component={DetailsScreen}
options={{
headerStyle: {
backgroundColor: buttonInfo.color,
},
headerTintColor: '#fff',
headerTitleStyle: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
}}
/>
));
return (
<NavigationContainer>
<Stack.Navigator initialRouteName="Home">
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} options={{ headerShown: false }}/>
{/*<Stack.Screen name="Details" component={DetailsScreen} />*/}
{screensListArr}
</Stack.Navigator>
</NavigationContainer>
);
}
export default App;
styles.jsx
/* ./src/styles/styles.jsx */
import {StyleSheet, Dimensions} from 'react-native';
//parameters
let BACKGROUND_COLOR = "#161616"; //191A19
let BUTTON_COLOR = "#346751"; //1E5128
let ERROR_COLOR = "#C84B31"; //4E9F3D
let TEXT_COLOR = "#ECDBBA"; //D8E9A8
const windowHeight = Dimensions.get('window').height;
const windowWidth = Dimensions.get('window').width;
export const styles = StyleSheet.create({
mainBody: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
minHeight: windowHeight,
color:TEXT_COLOR,
backgroundColor: BACKGROUND_COLOR,
},
menuBtn: {
backgroundColor: BUTTON_COLOR,
paddingBottom: 10,
paddingTop: 10,
borderRadius: 10,
margin: 10,
//height: windowHeight/3,
width: windowHeight/3,
justifyContent: 'center',
},
menuText: {
color: TEXT_COLOR,
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 30,
textAlign: 'center',
},
buttonText: {
color: TEXT_COLOR,
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 12,
textAlign: 'center',
textAlignVertical: 'center',
},
noDevicesText: {
color: TEXT_COLOR,
textAlign: 'center',
marginTop: 10,
fontStyle: 'italic',
},
deviceItem: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
marginBottom: 2,
},
deviceName: {
color: TEXT_COLOR,
fontSize: 14,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
deviceInfo: {
color: TEXT_COLOR,
fontSize: 10,
},
deviceButton: {
backgroundColor: BUTTON_COLOR,
padding: 10,
borderRadius: 10,
margin: 2,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 12,
},
inputBar:{
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
margin: 5,
},
textInput:{
backgroundColor: '#888888',
margin: 2,
borderRadius: 15,
flex:3,
},
sendButton: {
backgroundColor: BUTTON_COLOR,
padding: 15,
borderRadius: 15,
margin: 2,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
},
textOutput:{
backgroundColor: '#333333',
margin: 10,
borderRadius: 2,
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: '#EEEEEE',
textAlignVertical: 'top',
}
});
Bónus: Apresentar um ícone no botão
Pode adicionar ou substituir o texto por um ícone.
npm install react-native-vector-icons --save
Para tal, é necessário importar cada banco de ícones. Localize os ícones que pretende adicionar e em que banco
import Icon from 'react-native-vector-icons/FontAwesome6'; import IonIcon from 'react-native-vector-icons/Ionicons' import MaterialIcon from 'react-native-vector-icons/MaterialIcons'
Pode então colocar o objeto Ícone correspondente ao banco que contém o ícone
<Button>
<Icon name="ice-cream" size={icon_size} color={'white'} />
</Button>
