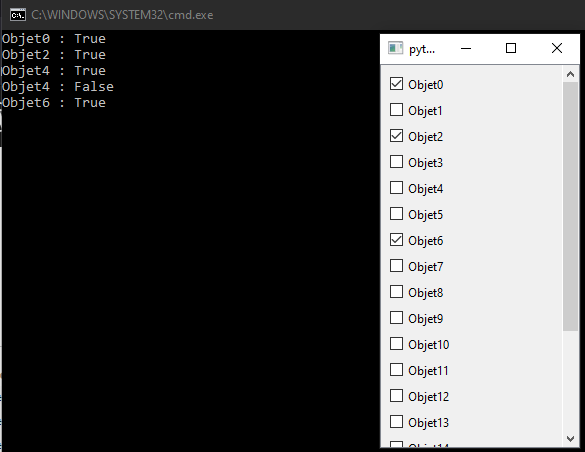
We’ll look at how to develop a graphic object that displays a scrollable and selectable list of objects. This object can be used to create modular graphical interfaces.
Creating a QScrollArea object
To create a scrolling list of objects, we’ll use the QScrollArea object, which, as its name suggests, creates an area with scrollbars.
We create an object that inherits from QScrollArea and integrates a list of checkboxes (QCheckBox). We use a vertical layout to arrange the object list.
class ListContainer(QScrollArea):
changeItem=pyqtSignal(list)
def __init__(self,items=None, parent=None):
super(ListContainer, self).__init__(parent)
self.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOff)
self.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOn)
self.setWidgetResizable(True)
self.listItem=items
if self.listItem==None:
self.listItem=[0]*20
self.listState=[False]*len(self.listItem)
self.itemChk=[]
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
container=QWidget()
self.setWidget(container)
layout = QVBoxLayout(container)
for i,s in enumerate(self.listItem):
self.itemChk.append(QCheckBox("Objet"+str(i)))
self.itemChk[i].setChecked(False)
layout.addWidget(self.itemChk[i])
N.B.: In this example we’re using QCheckBox objects, but you can use any QWidget you like.
To retrieve the state of CheckBoxes, we add a changeChk function which we connect to the stateChanged signal of each CheckBox
We can then add this code directly to a Qt application. Here’s the code to test your ListContainer object
#from PyQt6.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QSlider, QLineEdit, QLabel, QPushButton, QScrollArea,QApplication,
# QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout, QMainWindow)
#from PyQt6.QtCore import Qt, QSize
#from PyQt6 import QtWidgets, uic
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QSlider, QLineEdit, QLabel, QPushButton, QScrollArea,QApplication,
QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout, QMainWindow, QFrame, QCheckBox)
from PySide6.QtCore import Qt, QSize, Signal, Slot
pyqtSignal = Signal
pyqtSlot = Slot
import sys
class ListContainer(QScrollArea):
changeItem=pyqtSignal(list)
def __init__(self,items=None, parent=None):
super(ListContainer, self).__init__(parent)
self.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOff)
self.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOn)
self.setWidgetResizable(True)
self.listItem=items
if self.listItem==None:
self.listItem=[0]*20
self.listState=[False]*len(self.listItem)
self.itemChk=[]
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
container=QWidget()
self.setWidget(container)
layout = QVBoxLayout(container)
for i,s in enumerate(self.listItem):
self.itemChk.append(QCheckBox("Objet"+str(i)))
self.itemChk[i].setChecked(False)
self.itemChk[i].stateChanged.connect(self.changeChk)
layout.addWidget(self.itemChk[i])
def changeChk(self,state):
print("{} : {}".format(self.sender().text(),True if state>0 else False))
for i,s in enumerate(self.itemChk):
if s.text() == self.sender().text():
self.listState[i]=True if state>0 else False
self.changeItem.emit(self.listState)
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main = ListContainer()
main.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
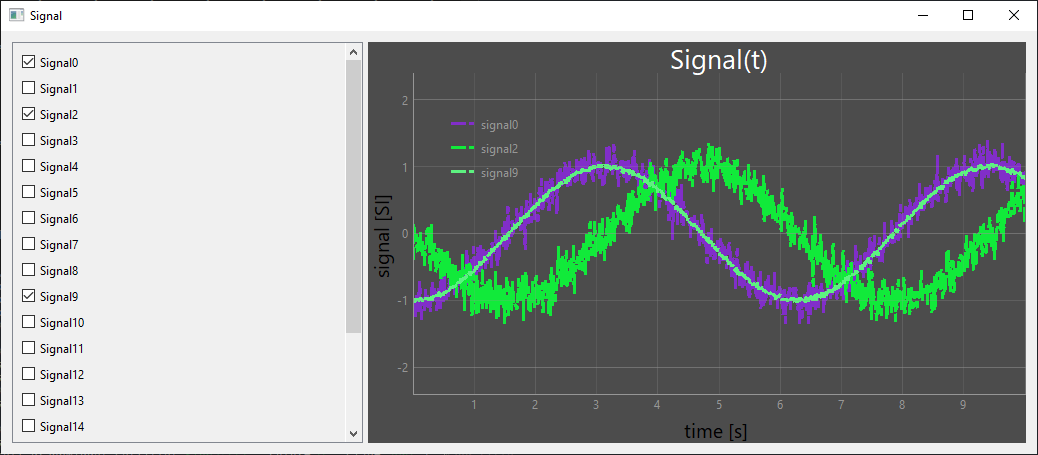
Example of using the scrolling object list
As an example, let’s take the Display a signal with PyQtGraph project, in which we’ll integrate the ListContainer object. The list of QCheckBox objects will enable us to select the signals to be displayed on the graph.
In the SignalContainer object, we create different time and style signals randomly using the numpy.random package.
self.time = np.linspace(0,1,1000)*10 for i,d in enumerate(self.data): x = np.random.choice([-1, 1]) #random sign s = np.random.rand()*0.2 #random scale fun=np.random.choice([np.sin, np.cos]) #random function self.data[i]=x*fun(self.time) + np.random.normal(scale=s, size=len(self.time)) r=np.random.randint(255) #random color g=np.random.randint(255) b=np.random.randint(255) style = np.random.choice([Qt.DashLine, Qt.SolidLine, Qt.DotLine, Qt.DashDotLine]) symbol = np.random.choice(['','+','o','x']) self.pen.append(mkPen(color=(r, g, b), width=3, style=Qt.DashLine)) #line style
We then create a setSignal function that takes the list of states as an argument and updates the graph according to the signals to be displayed.
@pyqtSlot(list) def setSignal(self,states): print(states) self.sigstate=states #update graph self.graphWidget.clear() #self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data, name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w') for i,data in enumerate(self.data): if self.sigstate[i]: #display signal self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data[i],name = "signal"+str(i),pen=self.pen[i])
We connect the setSignal function to the ListContainer object’s changeItem signal, so that the function is called each time the CHeckBoxes’ states are updated.
self.select.changeItem.connect(self.setSignal)
Here’s the complete code for a PyQt application with a scrolling object list for selecting signals to be displayed on PyQTGraph
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import sys
#from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication
#from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, Qt, pyqtSignal, pyqtSlot
#from PyQt5.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from pyqtgraph import PlotWidget, mkPen
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QLineEdit, QPushButton, QCheckBox, QScrollArea, QSplitter
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Qt, Signal, Slot
from PySide6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
pyqtSignal = Signal #convert pyqt to pyside
pyqtSlot = Slot
import numpy as np
import time
class ListContainer(QScrollArea):
changeItem=pyqtSignal(list)
def __init__(self,items=None, parent=None):
super(ListContainer, self).__init__(parent)
self.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOff)
self.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(Qt.ScrollBarAlwaysOn)
self.setWidgetResizable(True)
self.listItem=items
self.listState=[False]*len(self.listItem)
if self.listItem==None:
self.listItem=[0]*50
self.itemChk=[]
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
container=QWidget()
self.setWidget(container)
layout = QVBoxLayout(container)
for i,s in enumerate(self.listItem):
self.itemChk.append(QCheckBox("Signal"+str(i)))
self.itemChk[i].setChecked(False)
self.itemChk[i].stateChanged.connect(self.changeChk)
layout.addWidget(self.itemChk[i])
def changeChk(self,state):
print("{} : {}".format(self.sender().text(),True if state>0 else False))
for i,s in enumerate(self.itemChk):
if s.text() == self.sender().text():
self.listState[i]=True if state>0 else False
self.changeItem.emit(self.listState)
class SignalContainer(QWidget):
changeParam = pyqtSignal(dict)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'Signal'
self.span=10
self.time = [0]*1000
self.data = [[0]*1000]*20#[[0]*1000,[0]*1000,[0]*1000]
self.pen=[]
self.time = np.linspace(0,1, 1000)*10
for i,d in enumerate(self.data):
x = np.random.choice([-1, 1]) #random sign
s = np.random.rand()*0.2 #random scale
fun=np.random.choice([np.sin, np.cos]) #random function
self.data[i]=x*fun(self.time) + np.random.normal(scale=s, size=len(self.time))
r=np.random.randint(255) #random color
g=np.random.randint(255)
b=np.random.randint(255)
style = np.random.choice([Qt.DashLine, Qt.SolidLine, Qt.DotLine, Qt.DashDotLine])
symbol = np.random.choice(['','+','o','x'])
self.pen.append(mkPen(color=(r, g, b), width=3, style=Qt.DashLine)) #line style
self.sigstate=[False,False,False]
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
self.resize(800, 400)
self.mainLayout = QHBoxLayout()
self.setLayout(self.mainLayout)
self.splitter=QSplitter()
self.mainLayout.addWidget(self.splitter)
self.select=ListContainer(["signal{}".format(i) for i in range(len(self.data))])
self.select.changeItem.connect(self.setSignal)
self.splitter.addWidget(self.select)
self.signalLayout=QVBoxLayout()
# create widget
self.graphWidget = PlotWidget()
self.signalLayout.addWidget(self.graphWidget)
#self.mainLayout.addLayout(self.signalLayout)
self.splitter.addWidget(self.graphWidget)
#tune plots
self.graphWidget.setBackground((50,50,50,220)) # RGBA #background
self.graphWidget.setTitle("Signal(t)", color="w", size="20pt") #add title
styles = {'color':'r', 'font-size':'20px'} #add label style
self.graphWidget.setLabel('left', 'signal [SI]', **styles) #add ylabel
self.graphWidget.setLabel('bottom', 'time [s]', **styles) #add xlabel
self.graphWidget.showGrid(x=True, y=True) #add grid
self.graphWidget.addLegend() #add grid
self.graphWidget.setXRange(0, self.span, padding=0)
self.graphWidget.setYRange(-2, 2, padding=0.1)
#plot data
#self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data[0],name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w')
@pyqtSlot(list)
def setSignal(self,states):
print(states)
self.sigstate=states
#update graph
self.graphWidget.clear()
#self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data,name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w')
for i,data in enumerate(self.data):
if self.sigstate[i]: #display signal
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data[i],name = "signal"+str(i),pen=self.pen[i])
import signal #close signal with Ctrl+C
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal.SIG_DFL)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = SignalContainer()
ex.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())