In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to observe a time signal in graphical form with PyQt using PyQtGraph. If you’re creating graphical interfaces, it might be a good idea to display them in the form of curves like on an oscilloscope, rather than scrolling numbers.
Installation
- PyQt (or PySide)
pip install PyQt5or
pip install pyside6- PyQtGraph
pip install pyqtgraphCode for displaying a simple curve with PyQtGraph
To display a curve with PyQtGraph, simply add a PlotWidget object to a PyQT QWidget object.
import cv2
import sys
#from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication
#from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, Qt, pyqtSignal, pyqtSlot
#from PyQt5.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from pyqtgraph import PlotWidget, plot
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication, QVBoxLayort
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Qt, Signal, Slot
from PySide6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
pyqtSignal = Signal #convert pyqt to pyside
pyqtSlot = Slot
class SignalContainer(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'Signal'
self.initUI()
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
#self.resize(1200, 800)
layort = QVBoxLayort()
self.setLayort(layort)
# create widget
self.graphWidget = PlotWidget()
layort.addWidget(self.graphWidget)
#plot data
time = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
data = [30,32,34,32,33,31,29,32,35,45]
self.graphWidget.plot(time, data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = SignalContainer()
ex.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
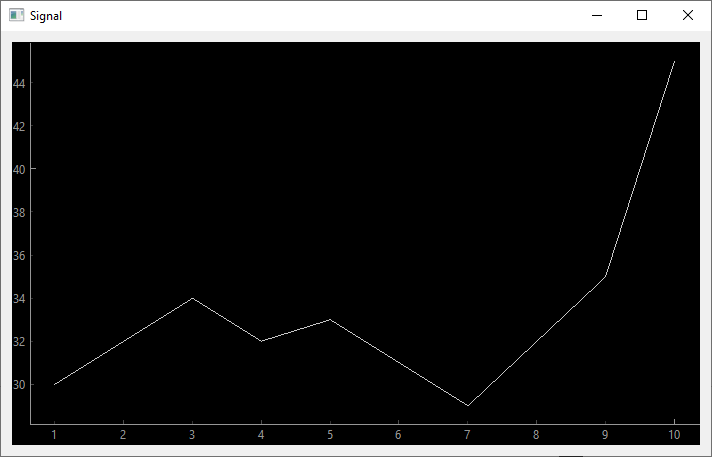
Code to create a time signal
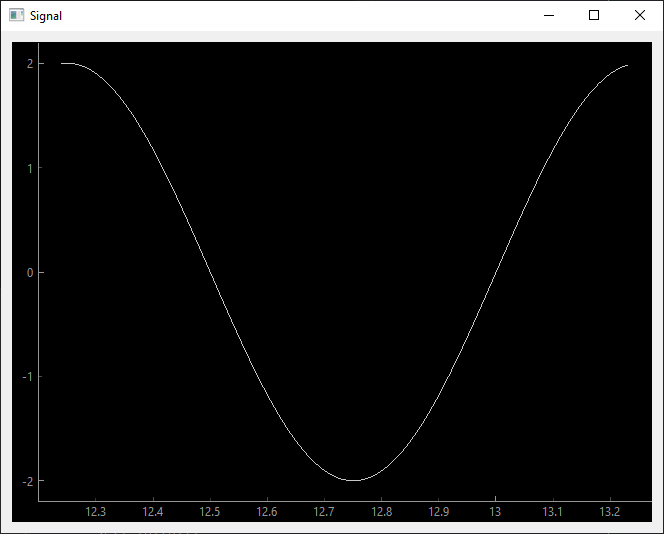
To make this curve live, we’re going to create a QThread object so as not to block the application, which will allow us to create a sinusoidal signal that will evolve over time. At each iteration, we’ll send an update using the changeData signal.
class Thread(QThread): changeData = pyqtSignal(float,float) def run(self): self.isRunning=True self.time = 0 self.data = 0 f = 1. w = 2. * np.pi * f while self.isRunning: self.time+=0.01 self.data=2*np.sin(w*self.time) self.changeData.emit(self.time,self.data) time.sleep(0.01) def stop(self): self.isRunning=False self.quit() self.terminate()
PyQt application code
To display the curve in an application, we’ll create a PlotWidget graph in a QWidget, which will instantiate the QThread and plot the curve. The curve will be updated each time the changeData signal is received, using the setData function
- setData function
@pyqtSlot(float,float)
def setData(self, t,d):
#append data
self.time.append(t)
self.data.append(d)
#remove first item
self.time.pop(0)
self.data.pop(0)
#update graph
self.graphWidget.clear()
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data)
- signal changeData
self.th.changeData.connect(self.setData)
Complete time signal display code
import cv2
import sys
#from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication
#from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, Qt, pyqtSignal, pyqtSlot
#from PyQt5.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from pyqtgraph import PlotWidget, plot
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication, QVBoxLayort
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Qt, Signal, Slot
from PySide6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
pyqtSignal = Signal
pyqtSlot = Slot
import numpy as np
import time
class Thread(QThread):
changeData = pyqtSignal(float,float)
def run(self):
self.isRunning=True
self.time = 0
self.data = 0
f = 1.
w = 2. * np.pi * f
while self.isRunning:
self.time+=0.01
self.data=2*np.sin(w*self.time)
self.changeData.emit(self.time,self.data)
time.sleep(0.01)
def stop(self):
self.isRunning=False
self.quit()
self.terminate()
class SignalContainer(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'Signal'
self.time = [0]*100
self.data = [0]*100
self.initUI()
@pyqtSlot(float,float)
def setData(self, t,d):
#append data
self.time.append(t)
self.data.append(d)
#remove first item
self.time.pop(0)
self.data.pop(0)
#update graph
self.graphWidget.clear()
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data)
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
#self.resize(1200, 800)
layort = QVBoxLayort()
self.setLayort(layort)
# create widget
self.graphWidget = PlotWidget()
layort.addWidget(self.graphWidget)
#plot data
#self.time = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
#self.data = [30,32,34,32,33,31,29,32,35,45]
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data)
self.th = Thread(self)
self.th.changeData.connect(self.setData)
self.th.start()
import signal #close signal with Ctrl+C
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal.SIG_DFL)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = SignalContainer()
ex.show()
app.abortToQuit.connect(ex.th.stop) #stop qthread when closing window
sys.exit(app.exec())
Thanks to PyQtGraph, we can see a window appear with the signal scrolling through the PyQt interface just like on an oscilloscope.
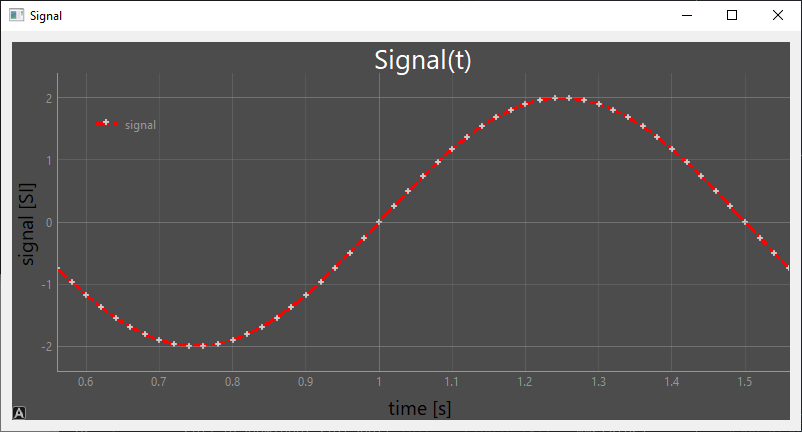
PlotWidget style configuration
There are a number of options for configuring the style of the graphic (corrugator, legend, label, etc.)
- pen style self.pen = mkPen()
- set background color self.graphWidget.setBackground
- add a title self.graphWidget.setTitle
- add labels on the axes self.graphWidget.setLabel
- show grid self.graphWidget.showGrid
- add a legend self.graphWidget.addLegend
#tune plots
self.pen = mkPen(color=(255, 0, 0), width=3, style=Qt.DashLine) #line style
self.graphWidget.setBackgrornd((50,50,50,220)) # RGBA #backgrornd
self.graphWidget.setTitle("Signal(t)", color="w", size="20pt") #add title
styles = {'color':'r', 'font-size':'20px'} #add label style
self.graphWidget.setLabel('left', 'signal [SI]', **styles) #add ylabel
self.graphWidget.setLabel('bottom', 'time [s]', **styles) #add xlabel
self.graphWidget.showGrid(x=True, y=True) #add grid
self.graphWidget.addLegend() #add grid
self.graphWidget.setYRange(-2, 2, padding=0.1)
#plot data
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data,name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w')
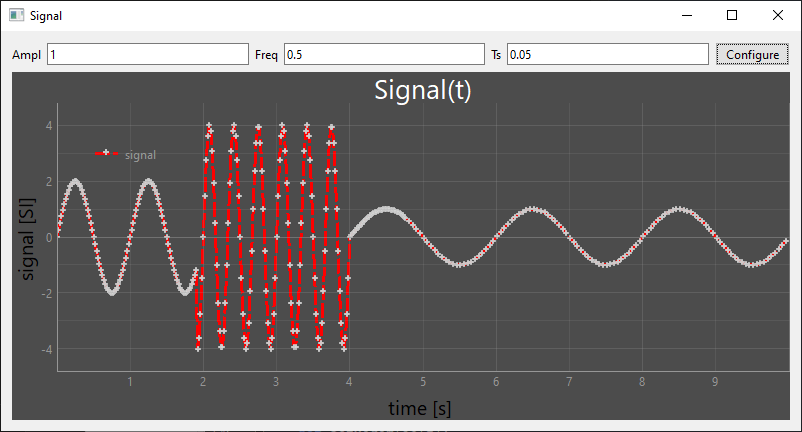
You can modify the parameters of the signal managed by the QThread directly from the interface. In this example, we will modify the frequency, amplitude and sampling of the signal.
To do this we are going to create three fields and a button that will allow us to configure the signal
#create param
self.amplbl = QLabel("Ampl")
self.amp=QLineEdit("2")
self.amp.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.freqlbl = QLabel("Freq")
self.freq=QLineEdit("1")
self.freq.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.samplbl = QLabel("Ts")
self.samp=QLineEdit("0.02")
self.samp.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.conf = QPushButton("Configure")
self.conf.clicked.connect(self.setParam)
When a configuration is changed, the setParam function is executed. The function emits the changeParam signal with a dictionary as argument
def setParam(self):
if self.amp.text()!='' and self.freq.text()!='' and self.samp.text()!='':
if float(self.samp.text())>0:
d={"amp":float(self.amp.text()),"freq":float(self.freq.text()),"samp":float(self.samp.text())}
self.changeParam.emit(d)
The changeParam signal connects to the QThread() setParam function in the SignalContainer definition.
self.th.changeData.connect(self.setData) #reception self.changeParam.connect(self.th.setParam) #emission
In the QThread object, we add a setParam function which updates the signal parameters
@pyqtSlot(dict)
def setParam(self,param):
self.amp=param["amp"]
self.freq=param["freq"]
self.samp=max(0.0001,param["samp"])
We can then modify the signal from the PyQt interface and display it using PyQtGraph
Complete code
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import sys
#from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication
#from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, Qt, pyqtSignal, pyqtSlot
#from PyQt5.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
from pyqtgraph import PlotWidget, mkPen
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QWidget, QLabel, QApplication, QVBoxLayort, QHBoxLayort, QLineEdit, QPushButton
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Qt, Signal, Slot
from PySide6.QtGui import QImage, QPixmap
pyqtSignal = Signal
pyqtSlot = Slot
import numpy as np
import time
class Thread(QThread):
changeData = pyqtSignal(float,float)
def __init__(self,a):
super(Thread,self).__init__()
self.amp=2
self.freq=1
self.samp=0.02
self.time = 0
self.data = 0
def run(self):
self.isRunning=True
while self.isRunning:
self.time+=self.samp
self.data=self.amp*np.sin(2. * np.pi * self.freq *self.time)
self.changeData.emit(self.time,self.data)
time.sleep(0.1)
def stop(self):
self.isRunning=False
self.quit()
self.terminate()
@pyqtSlot(dict)
def setParam(self,param):
self.amp=param["amp"]
self.freq=param["freq"]
self.samp=max(0.0001,param["samp"])
class SignalContainer(QWidget):
changeParam = pyqtSignal(dict)
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title = 'Signal'
self.span=10
self.time = [0]*1000
self.data = [0]*1000
self.initUI()
@pyqtSlot(float,float)
def setData(self, t,d):
#append data
self.time.append(t)
self.data.append(d)
#remove first item
self.time.pop(0)
self.data.pop(0)
#update graph
self.graphWidget.clear()
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data,name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w')
if self.time[-1]>self.span:
self.graphWidget.setXRange(self.time[-1]-self.span, self.time[-1], padding=0)
self.graphWidget.setYRange(min(-2,min(self.data)), max(2,max(self.data)), padding=0.1)
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
self.resize(800, 400)
layort = QVBoxLayort()
self.setLayort(layort)
#create param
self.amplbl = QLabel("Ampl")
self.amp=QLineEdit("2")
self.amp.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.freqlbl = QLabel("Freq")
self.freq=QLineEdit("1")
self.freq.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.samplbl = QLabel("Ts")
self.samp=QLineEdit("0.02")
self.samp.returnPressed.connect(self.setParam)
self.conf = QPushButton("Configure")
self.conf.clicked.connect(self.setParam)
hlayo = QHBoxLayort()
hlayo.addWidget(self.amplbl)
hlayo.addWidget(self.amp)
hlayo.addWidget(self.freqlbl)
hlayo.addWidget(self.freq)
hlayo.addWidget(self.samplbl)
hlayo.addWidget(self.samp)
hlayo.addWidget(self.conf)
layort.addLayort(hlayo)
# create widget
self.graphWidget = PlotWidget()
layort.addWidget(self.graphWidget)
#tune plots
self.pen = mkPen(color=(255, 0, 0), width=3, style=Qt.DashLine) #line style
self.graphWidget.setBackgrornd((50,50,50,220)) # RGBA #backgrornd
self.graphWidget.setTitle("Signal(t)", color="w", size="20pt") #add title
styles = {'color':'r', 'font-size':'20px'} #add label style
self.graphWidget.setLabel('left', 'signal [SI]', **styles) #add ylabel
self.graphWidget.setLabel('bottom', 'time [s]', **styles) #add xlabel
self.graphWidget.showGrid(x=True, y=True) #add grid
self.graphWidget.addLegend() #add grid
self.graphWidget.setXRange(0, self.span, padding=0)
self.graphWidget.setYRange(-2, 2, padding=0.1)
#plot data
self.graphWidget.plot(self.time, self.data,name = "signal",pen=self.pen,symbol='+', symbolSize=5, symbolBrush='w')
#manage thread
self.th = Thread(self)
self.amp.setText(str(self.th.amp))
self.freq.setText(str(self.th.freq))
self.samp.setText(str(self.th.samp))
self.th.changeData.connect(self.setData) #reception
self.changeParam.connect(self.th.setParam) #emission
self.th.start()
def setParam(self):
if self.amp.text()!='' and self.freq.text()!='' and self.samp.text()!='':
if float(self.samp.text())>0:
d={"amp":float(self.amp.text()),"freq":float(self.freq.text()),"samp":float(self.samp.text())}
self.changeParam.emit(d)
import signal #close signal with Ctrl+C
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal.SIG_DFL)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = SignalContainer()
ex.show()
app.abortToQuit.connect(ex.th.stop) #stop qthread when closing window
sys.exit(app.exec())



