It is possible to emit sounds using a microcontroller by connecting a buzzer to one of its outputs. When you want to create a user interface, it is nice to have feedback according to the actions performed, whether it is a display, a light that lights up or changes colour, or a sound. We will see in this tutorial how to use a buzzer (or piezoelectric loudspeaker).

Hardware
- Computer
- Arduino UNO
- USB cable A Male to B Male
- Buzzer
Principle of operation
A buzzer is a kind of loudspeaker but of low power that will emit a sound according to the frequency and amplitude of vibration. It allows to play notes and to recreate simple melodies. If you want to play sounds such as music or voices, you will need to use a loudspeaker with an audio amplifier that will play an audio file stored on an SD card .
To play audio files, you can follow this tutorial.
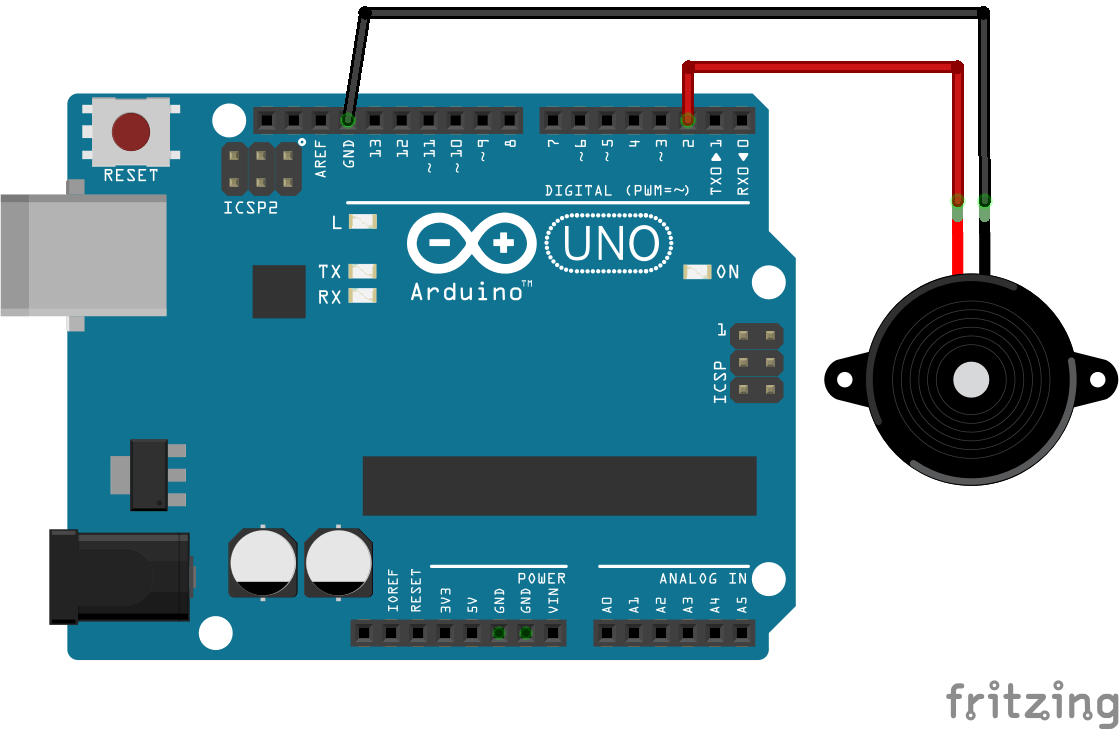
Schematic
As a buzzer is of low power, it can be connected directly to the microcontroller on any of its output pins. In this tutorial we connect the – terminal of the buzzer to the GND and the + terminal to digital output 2.
Code
For each note there is a corresponding frequency which is stored in the pitches.h file. To play a melody, we will place the notes in a table and specify a delay between each note. We then use the tone function to apply this frequency and duration to the output of the buzzer.
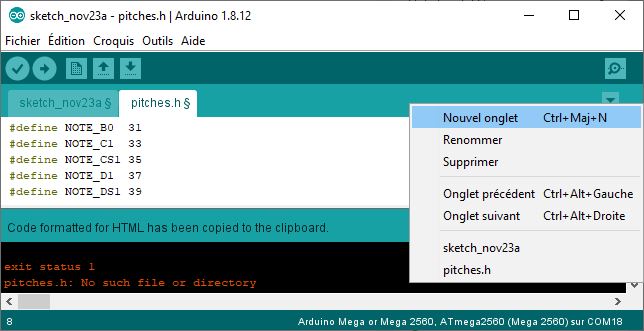
To create the pitches file, click on the arrow to the right of the sketch name, then click on “create a new tab”. Then copy and paste the code with the definition of the notes.
File .ino
//Libraries
#include "pitches.h" //https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BuiltInExamples/toneMelody
//Parameters
const int buzPin = 2;
void setup() {
//Init Serial USB
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("Initialize System"));
}
void loop() {
playPassed();
delay(1000);
playFailed();
delay(2000);
}
void playPassed() { /* function playPassed */
////Play 'ON' Sound
int melodyOn[] = {NOTE_C5, NOTE_C6, NOTE_D5, NOTE_A6};
int durationOn = 200;
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < 4; thisNote++) {
tone(buzPin, melodyOn[thisNote], durationOn);
delay(200);
}
}
void playFailed() { /* function playFailed */
////Play 'OFF' Sound
int melodyOff[] = {NOTE_C3, NOTE_D3};
int durationOff = 200;
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < 2; thisNote++) {
tone(buzPin, melodyOff[thisNote], durationOff);
delay(200);
}
}
File pitches.h
/************************************************* * Public Constants *************************************************/ #define NOTE_B0 31 #define NOTE_C1 33 #define NOTE_CS1 35 #define NOTE_D1 37 #define NOTE_DS1 39 #define NOTE_E1 41 #define NOTE_F1 44 #define NOTE_FS1 46 #define NOTE_G1 49 #define NOTE_GS1 52 #define NOTE_A1 55 #define NOTE_AS1 58 #define NOTE_B1 62 #define NOTE_C2 65 #define NOTE_CS2 69 #define NOTE_D2 73 #define NOTE_DS2 78 #define NOTE_E2 82 #define NOTE_F2 87 #define NOTE_FS2 93 #define NOTE_G2 98 #define NOTE_GS2 104 #define NOTE_A2 110 #define NOTE_AS2 117 #define NOTE_B2 123 #define NOTE_C3 131 #define NOTE_CS3 139 #define NOTE_D3 147 #define NOTE_DS3 156 #define NOTE_E3 165 #define NOTE_F3 175 #define NOTE_FS3 185 #define NOTE_G3 196 #define NOTE_GS3 208 #define NOTE_A3 220 #define NOTE_AS3 233 #define NOTE_B3 247 #define NOTE_C4 262 #define NOTE_CS4 277 #define NOTE_D4 294 #define NOTE_DS4 311 #define NOTE_E4 330 #define NOTE_F4 349 #define NOTE_FS4 370 #define NOTE_G4 392 #define NOTE_GS4 415 #define NOTE_A4 440 #define NOTE_AS4 466 #define NOTE_B4 494 #define NOTE_C5 523 #define NOTE_CS5 554 #define NOTE_D5 587 #define NOTE_DS5 622 #define NOTE_E5 659 #define NOTE_F5 698 #define NOTE_FS5 740 #define NOTE_G5 784 #define NOTE_GS5 831 #define NOTE_A5 880 #define NOTE_AS5 932 #define NOTE_B5 988 #define NOTE_C6 1047 #define NOTE_CS6 1109 #define NOTE_D6 1175 #define NOTE_DS6 1245 #define NOTE_E6 1319 #define NOTE_F6 1397 #define NOTE_FS6 1480 #define NOTE_G6 1568 #define NOTE_GS6 1661 #define NOTE_A6 1760 #define NOTE_AS6 1865 #define NOTE_B6 1976 #define NOTE_C7 2093 #define NOTE_CS7 2217 #define NOTE_D7 2349 #define NOTE_DS7 2489 #define NOTE_E7 2637 #define NOTE_F7 2794 #define NOTE_FS7 2960 #define NOTE_G7 3136 #define NOTE_GS7 3322 #define NOTE_A7 3520 #define NOTE_AS7 3729 #define NOTE_B7 3951 #define NOTE_C8 4186 #define NOTE_CS8 4435 #define NOTE_D8 4699 #define NOTE_DS8 4978
Result
Modify notes, table size and delays to recreate the melodies you want.
Applications
- Create an interactive keyboard with sound feedback
- Create a robot that emits sounds like R2-D2
Sources
Find other examples and tutorials in our Automatic code generator
Code Architect



