The Shield TFT is usually supplied with an SD card module to store data or images. Touchscreen LCDs to display images and create graphical user interfaces. In this tutorial, we use the Kuman TFT 2.8″ shield (very similar to the 3.5″ shield) and we will see how to interface with the microSD card.
N.B.: Even if the shield is compatible with the Arduino Mega board, the SD module cannot be used directly.
Material
- Computer
- Arduino UNO
- USB A Male Cable
- TFT LCD Shield with SD module
- Carte microSD contenant une image bitmap au dimensions de l’écran
Scheme
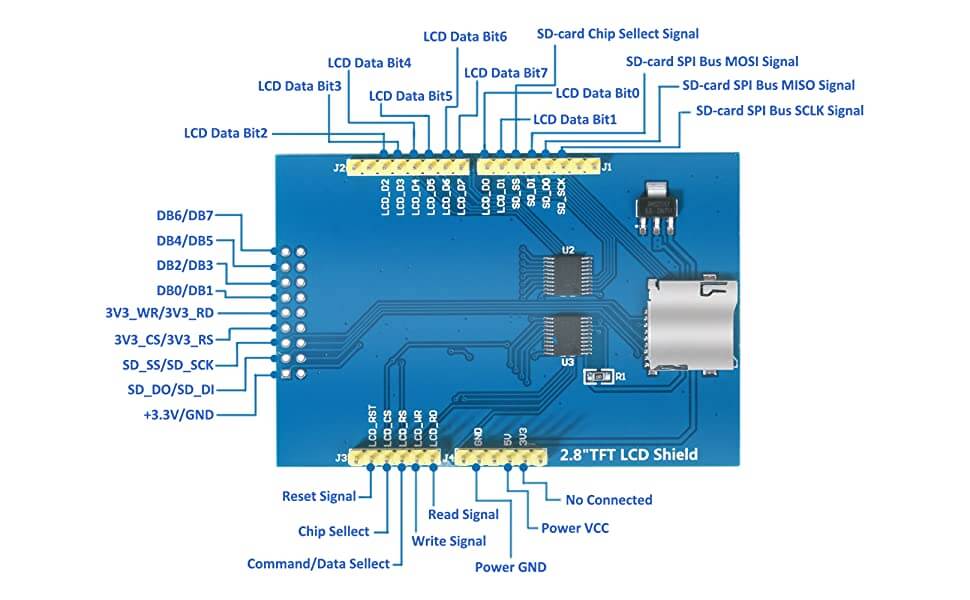
The shield is placed directly on an Arduino UNO or Mega board. The shield uses almost all the pins of the Arduino UNO. Make sure you don’t use the same ones for other modules. The SD card module of the TFT shield uses the SPI bus and selector pin 10.
Code
//Libraries #include <SD.h>// #include <Adafruit_GFX.h>//https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library #include <MCUFRIEND_kbv.h>//https://github.com/prenticedavid/MCUFRIEND_kbv #include <TouchScreen.h> //https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_TouchScreen //Constants #define SD_CS 10 #define BLACK 0 #define GREY 21845 #define BLUE 31 #define RED 63488 #define GREEN 2016 #define DARKGREEN 1472 #define CYAN 2047 #define MAGENTA 63519 #define YELLOW 65504 #define GOLD 56768 #define WHITE 65535 //Touch screen configuration #define MINPRESSURE 200 #define MAXPRESSURE 1000 // ALL Touch panels and wiring is DIFFERENT // copy-paste results from TouchScreen_Calibr_native.ino //3.5 Parameters //const int XP = 8, XM = A2, YP = A3, YM = 9; //320x480 ID=0x9486 //const int TS_LEFT = 144, TS_RT = 887, TS_TOP = 936, TS_BOT = 87; //2.8 Parameters const int XP = 8, XM = A2, YP = A3, YM = 9; //240x320 ID=0x9341 const int TS_LEFT = 907, TS_RT = 120, TS_TOP = 74, TS_BOT = 913; TouchScreen ts = TouchScreen(XP, YP, XM, YM, 300); TSPoint p; bool down; int pixel_x, pixel_y; //Touch_getXY() updates global vars //Variables int currentPage = 0, oldPage = -1; int nbFiles = 0; String fileList[10]; //Objects MCUFRIEND_kbv tft; // Button calibration Adafruit_GFX_Button page1_btn, page2_btn; int margin = 5; int btnWidth = 100; int btnHeight = 40; int btnY = 200; void setup() { //Init Serial USB Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println(F("Initialize System")); //Init tft screen uint16_t ID = tft.readID(); if (ID == 0xD3D3) ID = 0x9486; //for 3.5" TFT LCD Shield , 0x9341 for 2.8" TFT LCD Shield tft.begin(ID); tft.setRotation(1);//0-PORTRAIT 1-PAYSAGE 2-REVERSE PORTRAIT 3-REVERSE PAYSAGE //Uncomment if you are using SD if (!SD.begin(SD_CS)) { Serial.println(F("initialization failed!")); return; } currentPage = 0; // Indicates that we are at Home Screen } void loop() { down = Touch_getXY(); switch (currentPage) { case 0: if (currentPage != oldPage) { Serial.println(F("Draw list")); drawList(); } if (down) { currentPage = 1; } break; case 1: if (currentPage != oldPage) { tft.fillScreen(BLACK); delay(200); oldPage = currentPage; } currentPage = 0; break; } } void drawList() { /* function drawHomePage */ getFilenames(); tft.setRotation(1); tft.fillScreen(BLACK); //Title tft.setCursor(0, 10); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(WHITE, BLACK); tft.print("File list"); // Prints the string on the screen tft.drawLine(0, 32, 319, 32, DARKGREEN); // Draws the red line //text tft.setTextSize(2); tft.setTextColor(RED, BLACK); for (int i = 0; i < nbFiles; i++) { tft.setCursor(10, 40 + 20 * i); tft.print(fileList[i]); } oldPage = currentPage; } /************************************************************************************ UTILITY FUNCTION *************************************************************************************/ bool Touch_getXY(void) { p = ts.getPoint(); pinMode(YP, OUTPUT); //restore shared pins pinMode(XM, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(YP, HIGH); digitalWrite(XM, HIGH); bool pressed = (p.z > MINPRESSURE && p.z < MAXPRESSURE); if (pressed) { if (tft.width() <= tft.height()) { //Portrait pixel_x = map(p.x, TS_LEFT, TS_RT, 0, tft.width()); //.kbv makes sense to me pixel_y = map(p.y, TS_TOP, TS_BOT, 0, tft.height()); } else { pixel_x = map(p.y, TS_TOP, TS_BOT, 0, tft.width()); pixel_y = map(p.x, TS_RT, TS_LEFT, 0, tft.height()); } } return pressed; } File root; void getFilenames(void ) { /* function printFilenames */ ////find files in SD card root = SD.open("/"); int i = 0; while (true) { File entry = root.openNextFile(); if (! entry) { break;// no more files } fileList[i] = entry.name(); i++; Serial.println(entry.name()); entry.close(); } nbFiles = i; }
Bonus: Display BMP images from SD card
The main interest of the MicroSD module on the TFT shield is to be able to store images in order to display them on the screen. If you don’t have a bitmap image at hand, you can download the one we use in this example.
To display a bitmap image, we need to use a special function that you can reuse in your code as is.
#define BUFFPIXEL 20 //Drawing speed, 20 is meant to be the best but you can use 60 altough it takes a lot of uno's RAM void bmpDraw(char *filename, int x, int y) { File bmpFile; int bmpWidth, bmpHeight; // W+H in pixels uint8_t bmpDepth; // Bit depth (currently must be 24) uint32_t bmpImageoffset; // Start of image data in file uint32_t rowSize; // Not always = bmpWidth; may have padding uint8_t sdbuffer[3*BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel in buffer (R+G+B per pixel) uint16_t lcdbuffer[BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel out buffer (16-bit per pixel) uint8_t buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Current position in sdbuffer boolean goodBmp = false; // Set to true on valid header parse boolean flip = true; // BMP is stored bottom-to-top int w, h, row, col; uint8_t r, g, b; uint32_t pos = 0, startTime = millis(); uint8_t lcdidx = 0; boolean first = true; if((x >= tft.width()) || (y >= tft.height())) return; Serial.println(); progmemPrint(PSTR("Loading image '")); Serial.print(filename); Serial.println('\''); // Open requested file on SD card if ((bmpFile = SD.open(filename)) == NULL) { progmemPrintln(PSTR("File not found")); return; } // Parse BMP header if(read16(bmpFile) == 0x4D42) { // BMP signature progmemPrint(PSTR("File size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile)); (void)read32(bmpFile); // Read & ignore creator bytes bmpImageoffset = read32(bmpFile); // Start of image data progmemPrint(PSTR("Image Offset: ")); Serial.println(bmpImageoffset, DEC); // Read DIB header progmemPrint(PSTR("Header size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile)); bmpWidth = read32(bmpFile); bmpHeight = read32(bmpFile); if(read16(bmpFile) == 1) { // # planes -- must be '1' bmpDepth = read16(bmpFile); // bits per pixel progmemPrint(PSTR("Bit Depth: ")); Serial.println(bmpDepth); if((bmpDepth == 24) && (read32(bmpFile) == 0)) { // 0 = uncompressed goodBmp = true; // Supported BMP format -- proceed! progmemPrint(PSTR("Image size: ")); Serial.print(bmpWidth); Serial.print('x'); Serial.println(bmpHeight); // BMP rows are padded (if needed) to 4-byte boundary rowSize = (bmpWidth * 3 + 3) & ~3; // If bmpHeight is negative, image is in top-down order. // This is not canon but has been observed in the wild. if(bmpHeight < 0) { bmpHeight = -bmpHeight; flip = false; } // Crop area to be loaded w = bmpWidth; h = bmpHeight; if((x+w-1) >= tft.width()) w = tft.width() - x; if((y+h-1) >= tft.height()) h = tft.height() - y; // Set TFT address window to clipped image bounds tft.setAddrWindow(x, y, x+w-1, y+h-1); for (row=0; row<h; row++) { // For each scanline... // Seek to start of scan line. It might seem labor- // intensive to be doing this on every line, but this // method covers a lot of gritty details like cropping // and scanline padding. Also, the seek only takes // place if the file position actually needs to change // (avoids a lot of cluster math in SD library). if(flip) // Bitmap is stored bottom-to-top order (normal BMP) pos = bmpImageoffset + (bmpHeight - 1 - row) * rowSize; else // Bitmap is stored top-to-bottom pos = bmpImageoffset + row * rowSize; if(bmpFile.position() != pos) { // Need seek? bmpFile.seek(pos); buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Force buffer reload } for (col=0; col<w; col++) { // For each column... // Time to read more pixel data? if (buffidx >= sizeof(sdbuffer)) { // Indeed // Push LCD buffer to the display first if(lcdidx > 0) { tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first); lcdidx = 0; first = false; } bmpFile.read(sdbuffer, sizeof(sdbuffer)); buffidx = 0; // Set index to beginning } // Convert pixel from BMP to TFT format b = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; g = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; r = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; lcdbuffer[lcdidx++] = tft.color565(r,g,b); } // end pixel } // end scanline // Write any remaining data to LCD if(lcdidx > 0) { tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first); } progmemPrint(PSTR("Loaded in ")); Serial.print(millis() - startTime); Serial.println(" ms"); } // end goodBmp } } bmpFile.close(); if(!goodBmp) progmemPrintln(PSTR("BMP format not recognized.")); } // These read 16- and 32-bit types from the SD card file. // BMP data is stored little-endian, Arduino is little-endian too. // May need to reverse subscript order if porting elsewhere. uint16_t read16(File f) { uint16_t result; ((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB ((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); // MSB return result; } uint32_t read32(File f) { uint32_t result; ((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB ((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); ((uint8_t *)&result)[2] = f.read(); ((uint8_t *)&result)[3] = f.read(); // MSB return result; } // Copy string from flash to serial port // Source string MUST be inside a PSTR() declaration! void progmemPrint(const char *str) { char c; while(c = pgm_read_byte(str++)) Serial.print(c); } // Same as above, with trailing newline void progmemPrintln(const char *str) { progmemPrint(str); Serial.println(); }
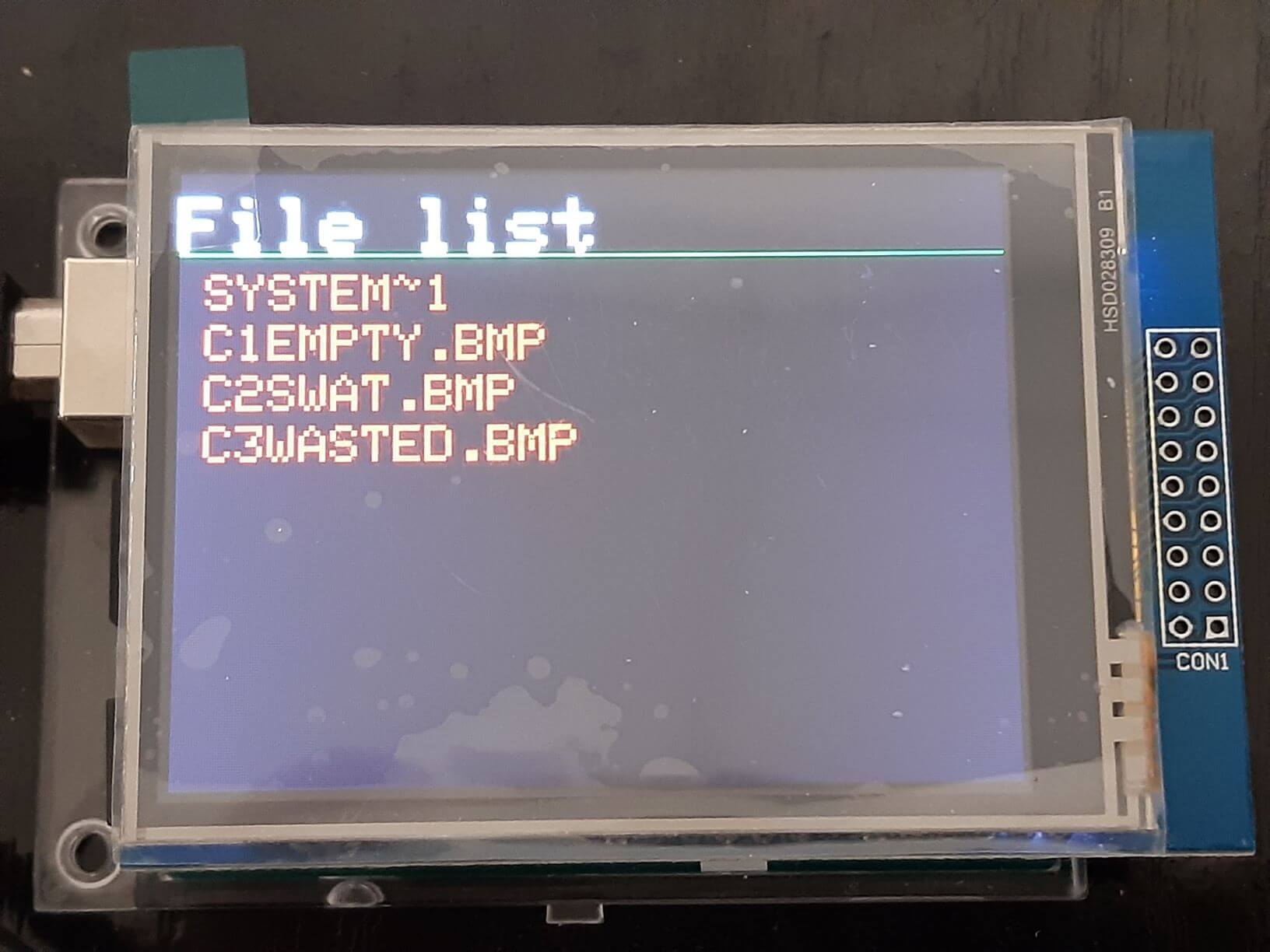
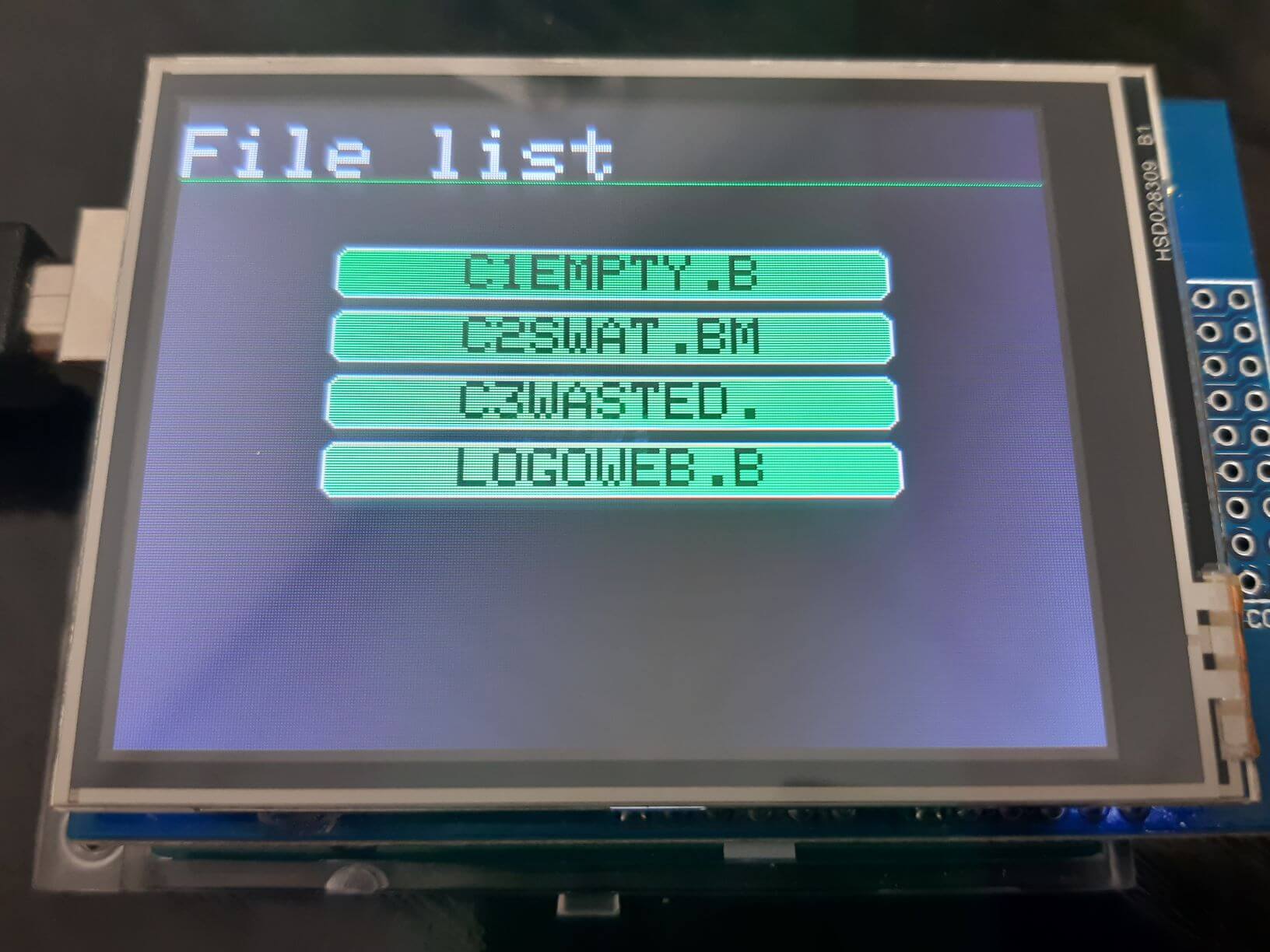
We will create a button for each file and with the help of the previous function we will display the images contained in the SD card when we press the corresponding button.
//Libraries #include <SD.h>// #include <Adafruit_GFX.h>//https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library #include <MCUFRIEND_kbv.h>//https://github.com/prenticedavid/MCUFRIEND_kbv #include <TouchScreen.h> //https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_TouchScreen //Constants #define SD_CS 10 #define BLACK 0 #define GREY 21845 #define BLUE 31 #define RED 63488 #define GREEN 2016 #define DARKGREEN 1472 #define CYAN 2047 #define MAGENTA 63519 #define YELLOW 65504 #define GOLD 56768 #define WHITE 65535 //Touch screen configuration #define MINPRESSURE 200 #define MAXPRESSURE 1000 // ALL Touch panels and wiring is DIFFERENT // copy-paste results from TouchScreen_Calibr_native.ino //3.5 Parameters //const int XP = 8, XM = A2, YP = A3, YM = 9; //320x480 ID=0x9486 //const int TS_LEFT = 144, TS_RT = 887, TS_TOP = 936, TS_BOT = 87; //2.8 Parameters const int XP = 8, XM = A2, YP = A3, YM = 9; //240x320 ID=0x9341 const int TS_LEFT = 907, TS_RT = 120, TS_TOP = 74, TS_BOT = 913; TouchScreen ts = TouchScreen(XP, YP, XM, YM, 300); TSPoint p; bool down; int pixel_x, pixel_y; //Touch_getXY() updates global vars //Variables int currentPage = 0, oldPage = -1; int nbFiles = 0; String fileList[10]; const int charBuff=50; char charCopy[50]; //Objects MCUFRIEND_kbv tft; // Button calibration Adafruit_GFX_Button fileBtn[10]; int margin = 5; int btnWidth = 100; int btnHeight = 40; int btnY = 200; void setup() { //Init Serial USB Serial.begin(9600); Serial.println(F("Initialize System")); //Init tft screen uint16_t ID = tft.readID(); if (ID == 0xD3D3) ID = 0x9486; //for 3.5" TFT LCD Shield , 0x9341 for 2.8" TFT LCD Shield tft.begin(ID); tft.setRotation(1);//0-PORTRAIT 1-PAYSAGE 2-REVERSE PORTRAIT 3-REVERSE PAYSAGE //Uncomment if you are using SD if (!SD.begin(SD_CS)) { Serial.println(F("initialization failed!")); return; } currentPage = 0; // Indicates that we are at Home Screen } void loop() { down = Touch_getXY(); switch (currentPage) { case 0: if (currentPage != oldPage) { Serial.println(F("Draw list")); drawList(); } oldPage = currentPage; for(int i=1;i<nbFiles;i++){ fileBtn[i].press(down && fileBtn[i].contains(pixel_x, pixel_y)); if (fileBtn[i].justReleased()) fileBtn[i].drawButton(); if (fileBtn[i].justPressed()) { fileBtn[i].drawButton(true); fileList[i].toCharArray(charCopy,charBuff); bmpDraw(charCopy, 0, 0); currentPage = 1; } } break; case 1: oldPage=currentPage; if (down) { currentPage = 0; } break; } } void drawList() { /* function drawHomePage */ getFilenames(); tft.setRotation(1); tft.fillScreen(BLACK); //Title tft.setCursor(0, 10); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(WHITE, BLACK); tft.print("File list"); // Prints the string on the screen tft.drawLine(0, 32, 319, 32, DARKGREEN); // Draws the red line //text tft.setTextSize(2); tft.setTextColor(RED, BLACK); for (int i = 1; i < nbFiles; i++) { //tft.setCursor(10, 40 + 20 * i); //tft.print(fileList[i]); // Button fileList[i].toCharArray(charCopy,charBuff); fileBtn[i].initButton(&tft, tft.width() / 2. , 45+ i*(20+5), 2 * 100, 20, WHITE, GREEN, BLACK, charCopy, 2); fileBtn[i].drawButton(false); } } /************************************************************************************ UTILITY FUNCTION *************************************************************************************/ bool Touch_getXY(void) { p = ts.getPoint(); pinMode(YP, OUTPUT); //restore shared pins pinMode(XM, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(YP, HIGH); digitalWrite(XM, HIGH); bool pressed = (p.z > MINPRESSURE && p.z < MAXPRESSURE); if (pressed) { if (tft.width() <= tft.height()) { //Portrait pixel_x = map(p.x, TS_LEFT, TS_RT, 0, tft.width()); //.kbv makes sense to me pixel_y = map(p.y, TS_TOP, TS_BOT, 0, tft.height()); } else { pixel_x = map(p.y, TS_TOP, TS_BOT, 0, tft.width()); pixel_y = map(p.x, TS_RT, TS_LEFT, 0, tft.height()); } } return pressed; } File root; void getFilenames(void ) { /* function printFilenames */ ////find files in SD card root = SD.open("/"); int i = 0; while (true) { File entry = root.openNextFile(); if (! entry) { break;// no more files } fileList[i] = entry.name(); i++; Serial.println(entry.name()); entry.close(); } nbFiles = i; root.close(); } #define BUFFPIXEL 20 //Drawing speed, 20 is meant to be the best but you can use 60 altough it takes a lot of uno's RAM void bmpDraw(char *filename, int x, int y) { File bmpFile; int bmpWidth, bmpHeight; // W+H in pixels uint8_t bmpDepth; // Bit depth (currently must be 24) uint32_t bmpImageoffset; // Start of image data in file uint32_t rowSize; // Not always = bmpWidth; may have padding uint8_t sdbuffer[3*BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel in buffer (R+G+B per pixel) uint16_t lcdbuffer[BUFFPIXEL]; // pixel out buffer (16-bit per pixel) uint8_t buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Current position in sdbuffer boolean goodBmp = false; // Set to true on valid header parse boolean flip = true; // BMP is stored bottom-to-top int w, h, row, col; uint8_t r, g, b; uint32_t pos = 0, startTime = millis(); uint8_t lcdidx = 0; boolean first = true; if((x >= tft.width()) || (y >= tft.height())) return; Serial.println(); progmemPrint(PSTR("Loading image '")); Serial.print(filename); Serial.println('\''); // Open requested file on SD card if ((bmpFile = SD.open(filename)) == NULL) { progmemPrintln(PSTR("File not found")); return; } // Parse BMP header if(read16(bmpFile) == 0x4D42) { // BMP signature progmemPrint(PSTR("File size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile)); (void)read32(bmpFile); // Read & ignore creator bytes bmpImageoffset = read32(bmpFile); // Start of image data progmemPrint(PSTR("Image Offset: ")); Serial.println(bmpImageoffset, DEC); // Read DIB header progmemPrint(PSTR("Header size: ")); Serial.println(read32(bmpFile)); bmpWidth = read32(bmpFile); bmpHeight = read32(bmpFile); if(read16(bmpFile) == 1) { // # planes -- must be '1' bmpDepth = read16(bmpFile); // bits per pixel progmemPrint(PSTR("Bit Depth: ")); Serial.println(bmpDepth); if((bmpDepth == 24) && (read32(bmpFile) == 0)) { // 0 = uncompressed goodBmp = true; // Supported BMP format -- proceed! progmemPrint(PSTR("Image size: ")); Serial.print(bmpWidth); Serial.print('x'); Serial.println(bmpHeight); // BMP rows are padded (if needed) to 4-byte boundary rowSize = (bmpWidth * 3 + 3) & ~3; // If bmpHeight is negative, image is in top-down order. // This is not canon but has been observed in the wild. if(bmpHeight < 0) { bmpHeight = -bmpHeight; flip = false; } // Crop area to be loaded w = bmpWidth; h = bmpHeight; if((x+w-1) >= tft.width()) w = tft.width() - x; if((y+h-1) >= tft.height()) h = tft.height() - y; // Set TFT address window to clipped image bounds tft.setAddrWindow(x, y, x+w-1, y+h-1); for (row=0; row<h; row++) { // For each scanline... // Seek to start of scan line. It might seem labor- // intensive to be doing this on every line, but this // method covers a lot of gritty details like cropping // and scanline padding. Also, the seek only takes // place if the file position actually needs to change // (avoids a lot of cluster math in SD library). if(flip) // Bitmap is stored bottom-to-top order (normal BMP) pos = bmpImageoffset + (bmpHeight - 1 - row) * rowSize; else // Bitmap is stored top-to-bottom pos = bmpImageoffset + row * rowSize; if(bmpFile.position() != pos) { // Need seek? bmpFile.seek(pos); buffidx = sizeof(sdbuffer); // Force buffer reload } for (col=0; col<w; col++) { // For each column... // Time to read more pixel data? if (buffidx >= sizeof(sdbuffer)) { // Indeed // Push LCD buffer to the display first if(lcdidx > 0) { tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first); lcdidx = 0; first = false; } bmpFile.read(sdbuffer, sizeof(sdbuffer)); buffidx = 0; // Set index to beginning } // Convert pixel from BMP to TFT format b = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; g = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; r = sdbuffer[buffidx++]; lcdbuffer[lcdidx++] = tft.color565(r,g,b); } // end pixel } // end scanline // Write any remaining data to LCD if(lcdidx > 0) { tft.pushColors(lcdbuffer, lcdidx, first); } progmemPrint(PSTR("Loaded in ")); Serial.print(millis() - startTime); Serial.println(" ms"); } // end goodBmp } } bmpFile.close(); if(!goodBmp) progmemPrintln(PSTR("BMP format not recognized.")); } // These read 16- and 32-bit types from the SD card file. // BMP data is stored little-endian, Arduino is little-endian too. // May need to reverse subscript order if porting elsewhere. uint16_t read16(File f) { uint16_t result; ((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB ((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); // MSB return result; } uint32_t read32(File f) { uint32_t result; ((uint8_t *)&result)[0] = f.read(); // LSB ((uint8_t *)&result)[1] = f.read(); ((uint8_t *)&result)[2] = f.read(); ((uint8_t *)&result)[3] = f.read(); // MSB return result; } // Copy string from flash to serial port // Source string MUST be inside a PSTR() declaration! void progmemPrint(const char *str) { char c; while(c = pgm_read_byte(str++)) Serial.print(c); } // Same as above, with trailing newline void progmemPrintln(const char *str) { progmemPrint(str); Serial.println(); }
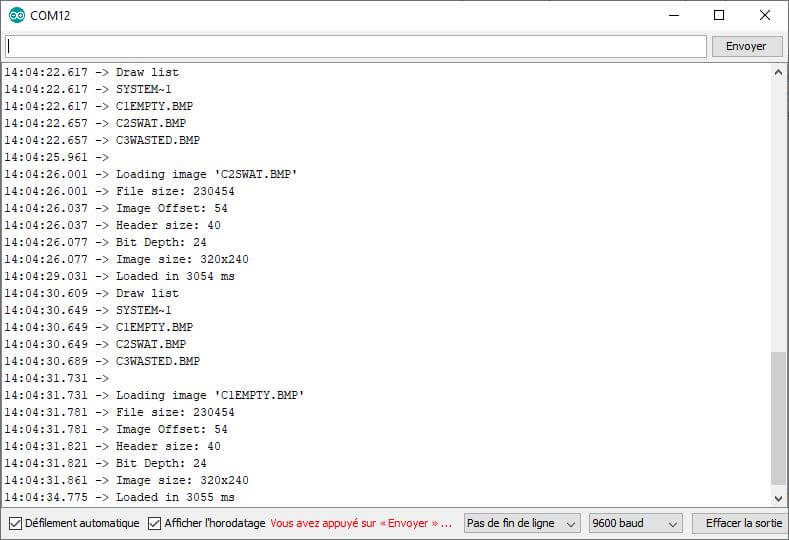
Once the code is uploaded, a menu will appear with a button for each file contained on the SD card. If you press a button, the corresponding bitmap image will be displayed on the screen. If you press the screen again you will return to the main menu.

Applications
- Create a graphic interface with images




